dm Server 2.0.0.M3 has been released, and is now available for download.
In the sprints since 2.0.0.M3, we've made significant progress towards the final release, both in terms of new features, and in defect fixes. Take a look at the M3 release notes if you're interested in seeing everything that we've been working on. Please keep your feedback coming as comments on our blog, in the forums, and on JIRA.
New and noteworthy
Integration of the OSGi Web Container reference implementation
dm Server now contains the
OSGi Web Container reference implementation and uses and builds upon it for all of its web support. As part of this work we've also moved to using the standard XML format for the configuration of Tomcat in dm Server.
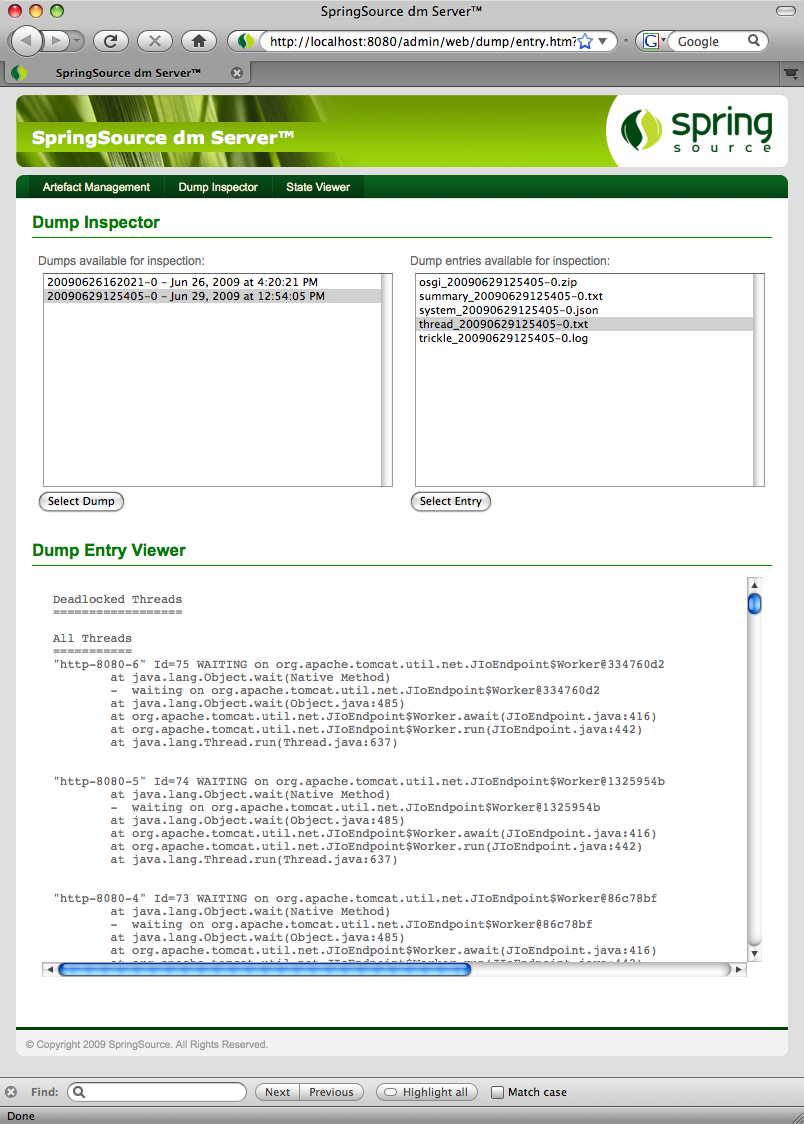
Dump analysis in the Admin Console
A new Dump Inspector has been added to dm Server's admin console. The Dump Inspector can be used to examine diagnostic dumps produced by dm Server's serviceability component.
Using Git as our version control system
We've recently moved dm Server's source code to Git as we felt that we could benefit significantly from Git's distributed nature and its excellent support for branches. If you're interested in accessing dm Server's source code, and in building dm Server from source, instructions for doing so now that the code is hosted in Git can be found below.
Documentation updates
A number of the newly-added features are now covered in the dm Server
user guide and
programmer guide.
Use of ConfigurationAdmin
dm Server now makes extensive use of ConfigurationAdmin to manage its configuration. This has resulted in changes to dm Server's configuration files and their format. The new files and format are described in the updated
user guide.
Updated application development guide
We've updated our
guide to creating an enterprise Java application with dm Server to bring it up-to-date with the 2.0 line.
Working with dm Server's source code
dm Server's Git repositories
| Repository URL | Contents |
|---|
| git://git.springsource.org/dm-server/util.git | General-purpose utility code |
| git://git.springsource.org/dm-server/artifact-repository | Artifact repository |
| git://git.springsource.org/dm-server/osgi-extensions.git | OSGi extensions and Equinox hooks |
| git://git.springsource.org/dm-server/kernel.git | dm Kernel |
| git://git.springsource.org/dm-server/web.git | OSGi Web Container integration and extensions |
| git://git.springsource.org/dm-server/servlet.git | Admin console |
| git://git.springsource.org/dm-server/hosted-repository | Hosted Artifact repository |
| git://git.springsource.org/dm-server/documentation.git | Documentation |
| git://git.springsource.org/dm-server/dm-server.git | Packaging |
Building dm Server from source
Setup
Before you can build dm Server from source, the following will have to be setup on your machine:
git clone git://git.springsource.org/dm-server/dm-server.git
cd dm-server
git checkout --track 2.0.0.M3 -b 2.0.0.M3
ant…

