Get ahead
VMware offers training and certification to turbo-charge your progress.
Learn moreReactor 3.6.0 is coming and going to be GA on November 14. This blogpost describes new features that are included in this upcoming release!
Today, everyone talks about Java 21 and Project Loom. The Project Reactor team hears that and sees value in that project within our ecosystem. With this upcoming release, we introduce support for the VirtualThread implementation.
Let's consider the following code sample:
package io.projectreactor.samples;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import reactor.core.scheduler.Schedulers;
public class LoomSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Flux.using(
() -> Files.lines(Paths.get(ClassLoader.getSystemResource("testfile.txt").toURI())),
Flux::fromStream,
Stream::close
)
.subscribeOn(Schedulers.boundedElastic())
.map(v -> Thread.currentThread() + " " + v)
.log()
.blockLast();
}
}
The code above reads all lines from the text file in reactive fashion. Unfortunately, the Files.lines method is a system I/O call that is known to be blocking. Therefore, we schedule all those operations on the shared Schedulers.boundedElastic() scheduler.
It is no secret that Schedulers.boundedElastic() is the main shared scheduler to offload all blocking calls you may do in the system. It is being used for simple HTTP blocking calls as well as for wrapping some inevitable blocking system interactions, such as generating a random UUID. However, it uses platform Thread instances by default which may add more contention to your system
Now, with Java 21+ and the new reactor-core 3.6.x, a new BoundedElasticThreadPerTaskScheduler implementation can replace the default one to use virtual threads instead of platform threads with Schedulers.boundedElastic(). All you need is to run your app on Java 21+ and set the -Dreactor.schedulers.defaultBoundedElasticOnVirtualThreads=true system property:
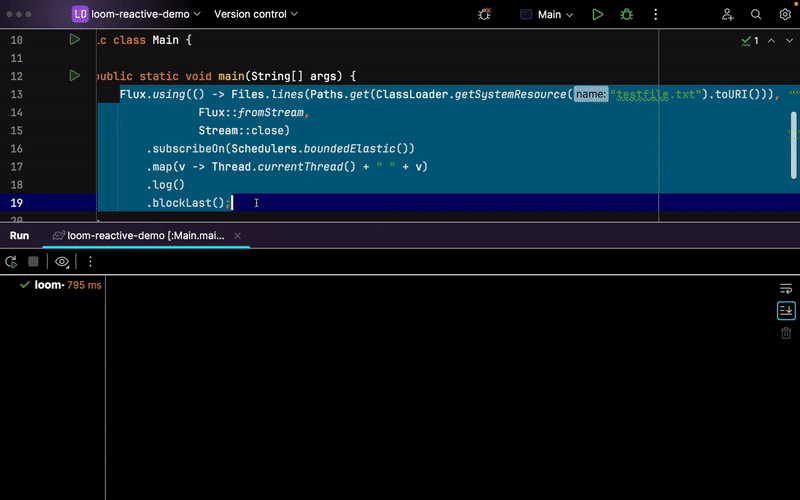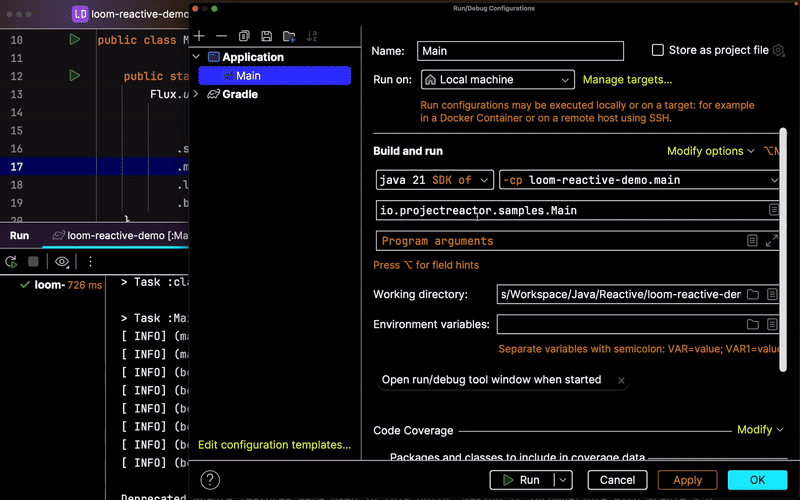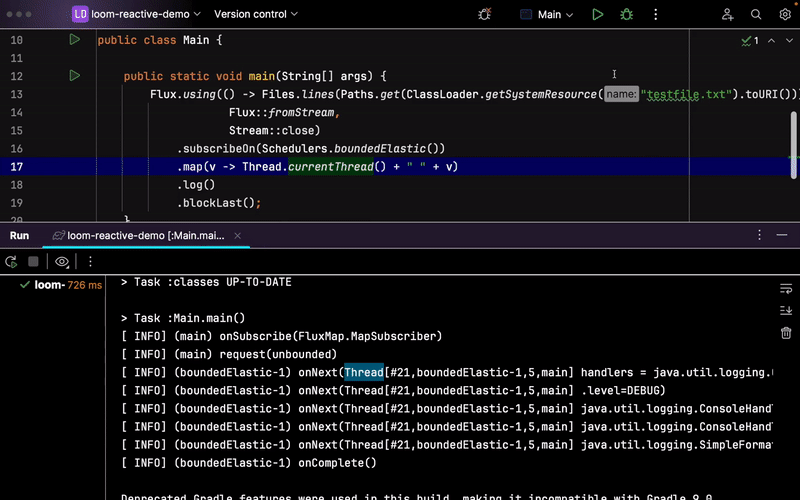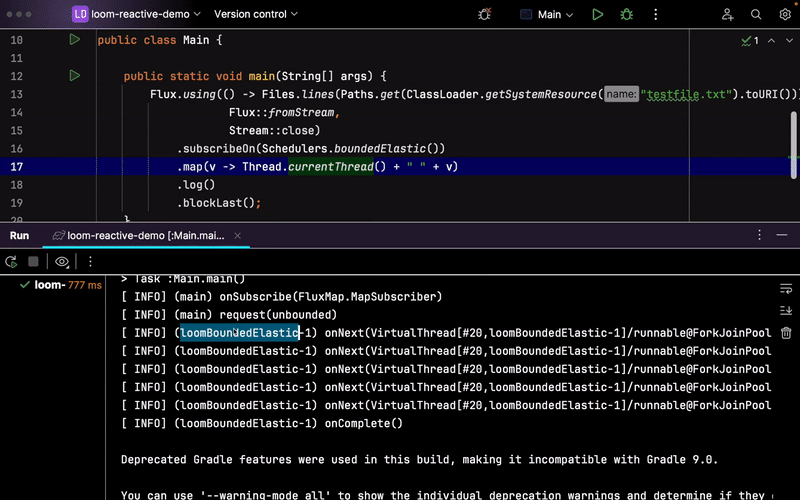
As you may have noticed, you will have a VirtualThread instance carrying scheduled work.
As you may have heard from our previous blogs starting from Reactor 3.5.0 we introduced a mechanism for automatic ThreadLocal restoration from Reactor Context in operators such as handle and tap. Later, in reactor 3.5.3 we added automatic restoration of ThreadLocal values within the whole set of operators available in Project Reactor:
static final ThreadLocal<String> TRACE_ID = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> "");
static {
ContextRegistry.getInstance()
.registerThreadLocalAccessor("TRACE_ID", TRACE_ID); <1>
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
logger.info("Setting Trace ID test-123-567-890");
TRACE_ID.set("test-123-567-890"); <1>
Hooks.enableAutomaticContextPropagation(); <2>
Mono.fromCallable(() -> {
logger.info("[" + TRACE_ID.get() + "] Generating UUID"); <4>
return UUID.randomUUID();
})
.subscribeOn(Schedulers.boundedElastic()) <3>
.doOnNext(v -> logger.info("[" + TRACE_ID.get() + "] " + "Generated UUID " + v)) <5>
.block();
}
The code above generates a random UUID that offloads <3> the blocking generation process on a dedicated worker. To enable automatic ThreadLocal propagation magic you need to have the Micrometer Context Propagation library available at the runtime, register <1> required ThreadLocal instances and then, call the Hooks API <2> to activate this specific propagation mode.
If we inspect the output of the code above, we see that the specified <1> TRACE_ID ThreadLocal is consistently available in all the places <3> <4> regardless of the Thread switch.
[ INFO] (main) Setting Trace ID test-123-567-890 <1>
[ INFO] (boundedElastic-1) [test-123-567-890] Generating UUID <2>
[ INFO] (boundedElastic-1) [test-123-567-890] Generated UUID baa79b8a-7808-4c27-a426-8464e4372269 <2>
Thread mainThread boundedElastic-1Although this mechanism is close enough to what everyone wants, it is limited by Reactor owned producers and transformers. To understand where it may not perfectly work, let’s modify our above sample and add integration with the external Reactive Streams-based library such as JDK11 HttpClient:
static HttpClient jdkHttpClient = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
static {
ContextRegistry.getInstance()
.registerThreadLocalAccessor("TRACE_ID", TRACE_ID);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
logger.info("Setting Trace ID");
TRACE_ID.set("test-123-567-890");
Hooks.enableAutomaticContextPropagation();
Mono.fromFuture(() -> {
logger.info("[" + TRACE_ID.get() + "] Preparing request");
return jdkHttpClient.sendAsync(HttpRequest.newBuilder() <1>
.uri(URI.create("https://httpbin.org/drip"))
.GET()
.build(),
HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofPublisher());
})
.flatMapMany(r -> {
logger.info("[" + TRACE_ID.get() + "] " + "Handling response[" + r.statusCode() + "] and reading body");
return FlowAdapters.toPublisher(r.body()); <2>
})
.collect(new ByteBufferToStringCollector()) <3>
.doOnNext(v -> logger.info("[" + TRACE_ID.get() + "] " + "Response body is " + v))
.block();
}
In the modified sample, we do a network call <1> and then read the response back. The response body is represented as a Flow.Publisher <2>, which we flatten and transform to string representation <3>. Once this code runs, one of the possible outputs may look as follows:
[ INFO] (main) Setting Trace ID test-123-567-890
[ INFO] (main) [test-123-567-890] Preparing request
[ INFO] (ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1) [test-123-567-890] Handling response[200] and reading body
[ INFO] (HttpClient-1-Worker-0) [] Response body is ********** <1>
What we can observe from the output is that, with reactor 3.5.3+, a consumption of an external Publisher may lead to context loss <1>, since we don't know whether we need to do extra lifting to restore lost ThreadLocal instances.
With reactor 3.6.x, this output is always consistent:
[ INFO] (main) Setting Trace ID test-123-567-890
[ INFO] (main) [test-123-567-890] Preparing request
[ INFO] (ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1) [test-123-567-890] Handling response[200] and reading body
[ INFO] (HttpClient-1-Worker-0) [test-123-567-890] Response body is ********** <1>
With this release, we reinforced the ThreadLocal values restoration mechanics and added extra logic that detects any external Publisher implementations. Once those are detected, we decorate them to ensure that you never lose ThreadLocal values while operating in our pipeline.
With reactor 3.6.x, we embraced multi-release jar (MRJ) support and already added improvements that eliminate reflection, where possible. We plan to expand MRJ usage and use all the JDK9+ features in the upcoming releases!
Stay tuned! All the sources could be found at Github