Get ahead
VMware offers training and certification to turbo-charge your progress.
Learn more(This blog post was written jointly by Phil Webb and Dave Syer).
We are pleased to announce the first milestone release of a new project called Spring Boot.
Spring Boot aims to make it easy to create Spring-powered, production-grade applications and services with minimum fuss. It takes an opinionated view of the Spring platform so that new and existing users can quickly get to the bits they need. You can use it to create stand-alone Java applications that can be started using 'java -jar' or more traditional WAR deployments. We also provide a command line tool that runs 'spring scripts'.
The diagram below shows Spring Boot as a point of focus on the larger Spring ecosystem. It presents a small surface area for users to approach and extract value from the rest of Spring:
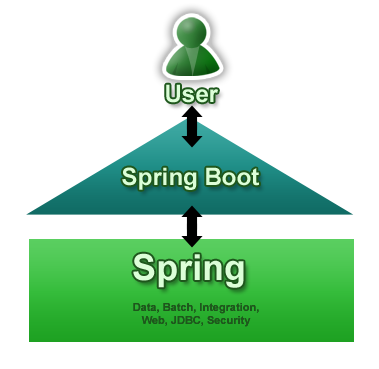
The primary goals of Spring Boot are:
Spring Boot does not generate code and there is absolutely no requirement for XML configuration.
Spring Boot ships with a small command line application that can be used to run 'spring scripts'. Spring scripts are written in Groovy, which means that you have a familiar Java-like syntax, without so much boilerplate code. We are able to deduce a lot of information simply by looking at the way you have written your script. For example, here is a simple web application:
@Controller
class ThisWillActuallyRun {
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
String home() {
return "Hello World!"
}
}
When you run this application using 'spring run webapp.groovy' a number things are happening:
'import' statements to save you typing them@ResponseBody annotation and download appropriate Spring JARs@Configuration that you would otherwise need to writeThe command line tool recognizes a number of different types of Spring Applications, including Web, Batch and Integration. There are a number of samples available in the GitHub repository.
You don't need use the command line tool or write Groovy code to get the benefits of Spring Boot. We also have first class Java support. For example, here is the same application written in Java:
import org.springframework.boot.*;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.*;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@Controller
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class SampleController {
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
String home() {
return "Hello World!";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(SampleController.class, args);
}
}
Other than import statements, the main difference between this example and the earlier Groovy script is the main() method that calls SpringApplication and the @EnableAutoConfiguration annotation.
Obviously with Java you also need a build system to compile and package your code. We provide a number of convenient 'starter' POMs that you can use with Maven, Gradle or Ant+Ivy to quickly grab appropriate dependencies. For example, the application above would need just a single dependency to the spring-boot-starter-web module.
We also provide Maven and Gradle plugins that allow you to package a fully self contained 'fat jar' that can be started from the command line:
$ java -jar myproject.jar . ____ _ __ _ _ /\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \ ( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \ \\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) ) ' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / / =========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/ :: Spring Boot :: v0.0.0.BUILD.SNAPSHOT 2013-07-31 00:08:16.117 INFO 56603 --- [ main] o.s.b.s.app.SampleApplication : Starting SampleApplication v0.1.0 on mycomputer with PID 56603 (/apps/myapp.jar started by pwebb) 2013-07-31 00:08:16.166 INFO 56603 --- [ main] ationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext : Refreshing org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext@6e5a8246: startup date [Wed Jul 31 00:08:16 PDT 2013]; root of context hierarchy
Spring Boot also includes helpful features that you often need when you push an application into production. We can automatically provide web endpoints that you can use to monitor application health, provide basic metrics or use to analyze production issues (such as thread deadlocks). We also provide a new @ConfigurationProperties annotation that you can use to externalize your application configuration (complete with support for JSR-303 @Valid annotations).
Spring Boot 0.5.0.M1 is available now in the Spring Milestone Repository. If you want to try out any of the examples in this blog head over to the GitHub project page where you find detailed instructions. We are actively looking for early feedback so please feel free to raise issues or fork the repository and submit pull requests.
Book your place at SpringOne in Santa Clara soon. It's simply the best opportunity to find out first hand all that's going on and to provide direct feedback. Expect a number of significant new announcements this year. Check recent blog posts to see what I mean and there is more to come!